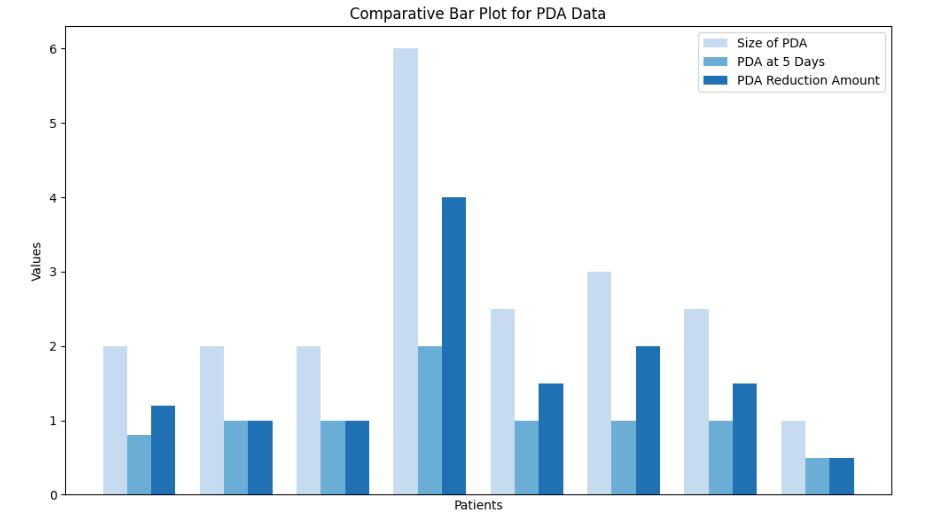
Figure I: Comparative Bar plot for PDA Data across Patients over 5 days
The study “Common Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease with Outcome in Sick Term and Preterm Neonates Admitted in NICU in Dhaka, Bangladesh” explores the prevalence, clinical complications, and treatment approaches for congenital heart disease (CHD) in neonates. Among 61 cases, atrial septal defect (ASD) was the most common (36.1%), followed by ventricular septal defect (VSD) (24.6%) and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) (19.7%). Respiratory distress (62.3%) and pneumonia (34.4%) were frequent complications, with oxygen therapy (68.9%) being the primary treatment. The study highlights the significant burden of CHD, especially in infants of diabetic mothers, and emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and echocardiographic monitoring to improve neonatal outcomes.
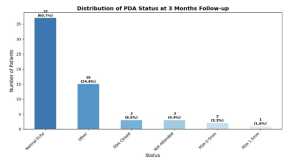
Figure 2: Distribution of PDA Status at 3-Month Follow-Up